Are you getting confused with VR, AR, XR and MR ?
Here is a quick guide about what really is the difference between XR/ AR / VR / MR technologies.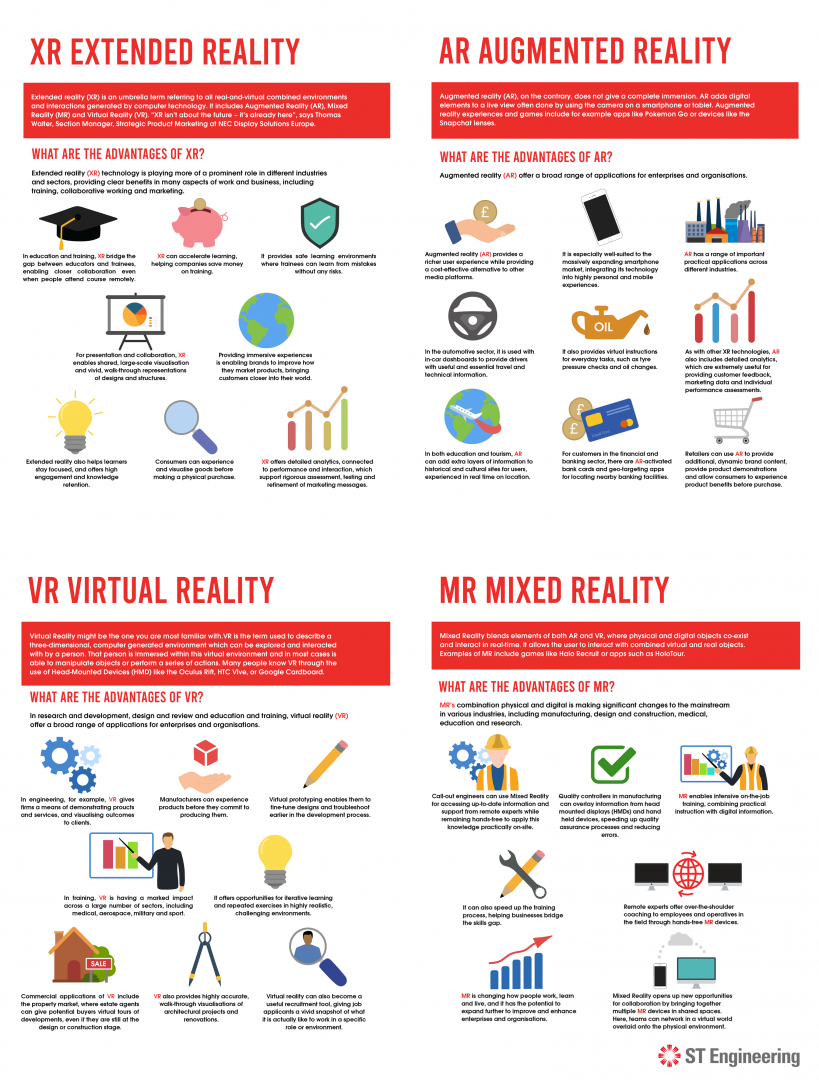
XR Extended Reality
Extended reality (XR) is an umbrella term referring to all real-and-virtual combined environments and interactions generated by computer technology. It includes Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR) and Virtual Reality (VR). "XR isn’t about the future - it’s already here", says Thomas Walter, section Manager, strategic product marketing at NEC Display Solutions Europe.What are the advantages of XR?
Extended reality (XR) technology is playing more of a prominent role in different industries and sectors, providing clear benefits in many aspects of work and business, including training, collaborative working and marketing. In education and training, XR bridges the gap between educators and trainees, enabling closer collaboration even when people attend courses remotely. XR can accelerate learning, helping companies save money on training. It provides safe learning environments where trainees can learn from mistakes without risk. Extended reality also helps learners stay focused, and offers high engagement and knowledge retention. For presentation and collaboration, XR enables shared, large-scale visualisation and vivid, walk-through representations of designs and structures. Providing immersive experiences is enabling brands to improve how they market products, bringing customers closer into their world. Consumers can experience and visualise goods before making a physical purchase. XR offers detailed analytics, connected to performance and interaction, which support rigorous assessment, testing and refinement of marketing messages.Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality might be the one you are most familiar with.VR is the term used to describe a three-dimensional, computer generated environment which can be explored and interacted with by a person. That person is immersed within this virtual environment and in most cases is able to manipulate objects or perform a series of actions. Many people know VR through the use of Head-Mounted Devices (HMD) like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or Google Cardboard. If you want to know more about HMDs, check out this blog article. What is less known by the public is that there are many different types of virtual reality systems, like VR Caves or VR theatres developed for use within scientific and engineering industries.
What are the advantages of VR?
In research and development, design and review and education and training, virtual reality (VR) offer a broad range of applications for enterprises and organisations. In engineering, for example, VR gives firms a means of demonstrating products and services, and visualising outcomes to clients. Manufacturers can experience products before they commit to producing them. Virtual prototyping enables them to fine-tune designs and troubleshoot earlier in the development process. In training, VR is having a marked impact across a large number of sectors, including medical, aerospace, military and sport. It offers opportunities for iterative learning and repeated exercises in highly realistic, challenging environments. Commercial applications of VR include the property market, where estate agents can give potential buyers virtual tours of developments, even if they are still at the design or construction stage. VR also provides highly accurate, walk-through visualisations of architectural projects and renovations. Virtual reality can also become a useful recruitment tool, giving job applicants a vivid snapshot of what it is actually like to work in a specific role or environment.- World-leading automotive supplier Hutchinson has installed immersive VR rooms from Antycip in its Innovation & Research Centre. The four-sided CAVE (Cave Automatic Virtual Environment) enables Hutchinson to enhance and develop how it prototypes its projects.
- Bath University now has a VR CAVE, consisting of an environmental chamber on a moving hydraulic platform. This is a valuable research tool, for studies that immerse people in different lifelike environments.
- Antycip has supplied a VR theatre to French higher education and research institute ENS Rennes for use to study sports team interaction and communication on the field.
Augmented Reality (AR)
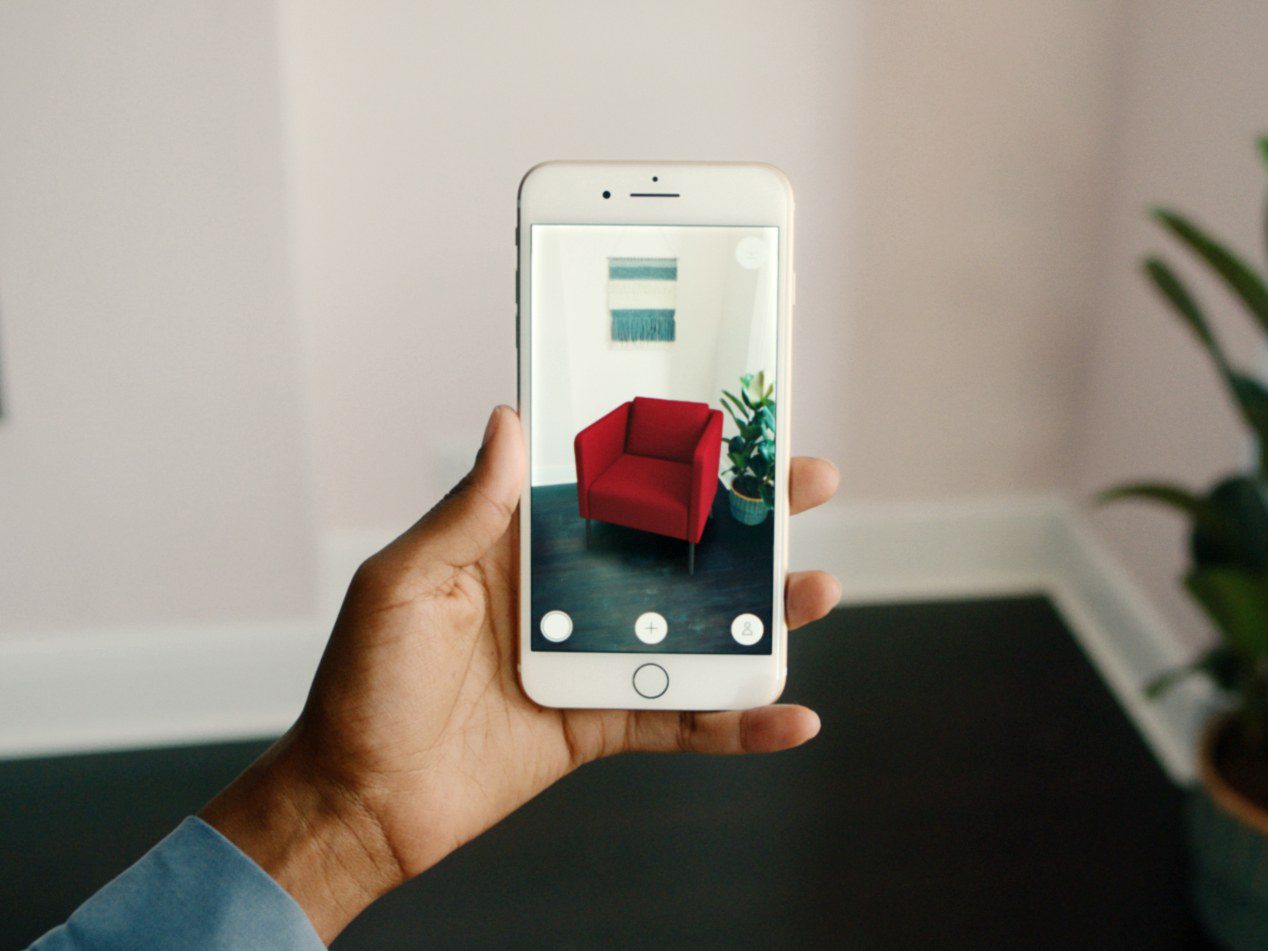
Augmented reality (AR), on the contrary, does not give a complete immersion. AR adds digital elements to a live view often done by using the camera on a smartphone or tablet. Augmented reality experiences and games include for example apps like Pokemon Go or devices like the Snapchat lenses.