A brief guide to VR motion tracking technology
Motion Tracking, the process of digitising your movements for use in computer software, is a key component of VR systems. Without VR motion tracking systems, you would find yourself restricted in the virtual world, unable to look around, move, and explore. Being able to engage and interact with the virtual world the moment you step into a VR CAVE or put on your VR headset – without being reminded of the real world – is crucial to the creation of a truly immersive experience.How does Motion Tracking work?
To understand how an object is able to move in three-dimensional space, we need to look at the concept of six degrees of freedom (6DoF), which refers to the freedom of movement of a rigid body in 3D space.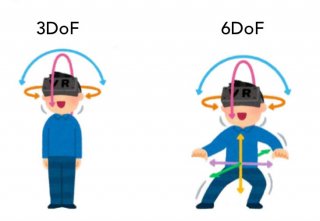 Essentially, the body is free to move forwards or backwards, up or down, and left to right - the three perpendicular axes, or 3DoF.
Essentially, the body is free to move forwards or backwards, up or down, and left to right - the three perpendicular axes, or 3DoF. This is then combined with rotation around these axes – or 6DoF. The virtual world must mimic the movements that we do in the real world, like using our hands, moving our heads, and moving around a room, but the degrees of immersion varies depending on the application: For some applications, like digital prototyping for the automotive industry, VR motion tracking is necessary and will either make or break your state of immersion.
In some other cases, a Virtual Reality or Simulation experience might need a more fixed approached, e.g. a flight simulator where the person is sat in a cockpit using a joystick. There are already different software and technologies to make the most of exploring a virtual environment, let’s look at the main two types of VR motion trackers and at how they work.

Which types of motion tracking technology exist today?
There are two different types of applications that support the tracking of movement: optical and non-optical motion tracking.Optical tracking
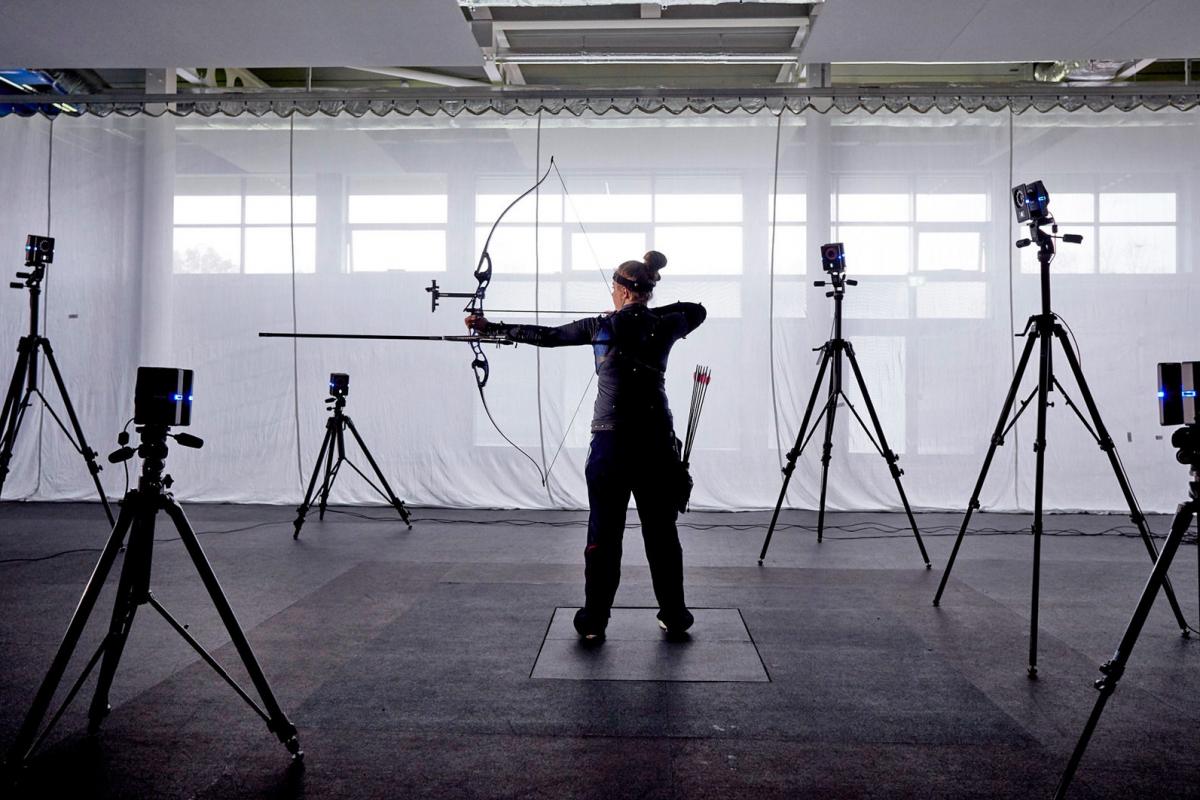
Optical tracking is where an imaging device is used to track body motion of an individual. The person who is being tracked is required to hold handheld controllers or an HMD (Head Mounted Display) that has the trackers on them or to wear optical markers, which are placed on certain parts of the body. More advanced options can also use sound waves or magnetic fields. To track movements of the user's point of view in a VR CAVE, we use a number of tracking cameras which send signals to adjust the images seen by the wearer as they move around the VR environment. To maintain the immersion in the VR environment, the tracking of the VR glasses needs to be highly accurate. Leading manufacturers like ART or Vicon specialise in this, and ensure that the user's viewpoint in the 3D behaves in the same way as it would in the real world. Any delay or latency, caused by inaccurate tracking, would cause a disconnection between the two.Non-optical tracking
Non-optical tracking makes use of microscopic electromechanical sensors that are installed in hardware or attached to the body to measure and track movements. These are typically gyroscopes, magnetometers, and accelerometers.




















